Echocardiogram (ECHO)
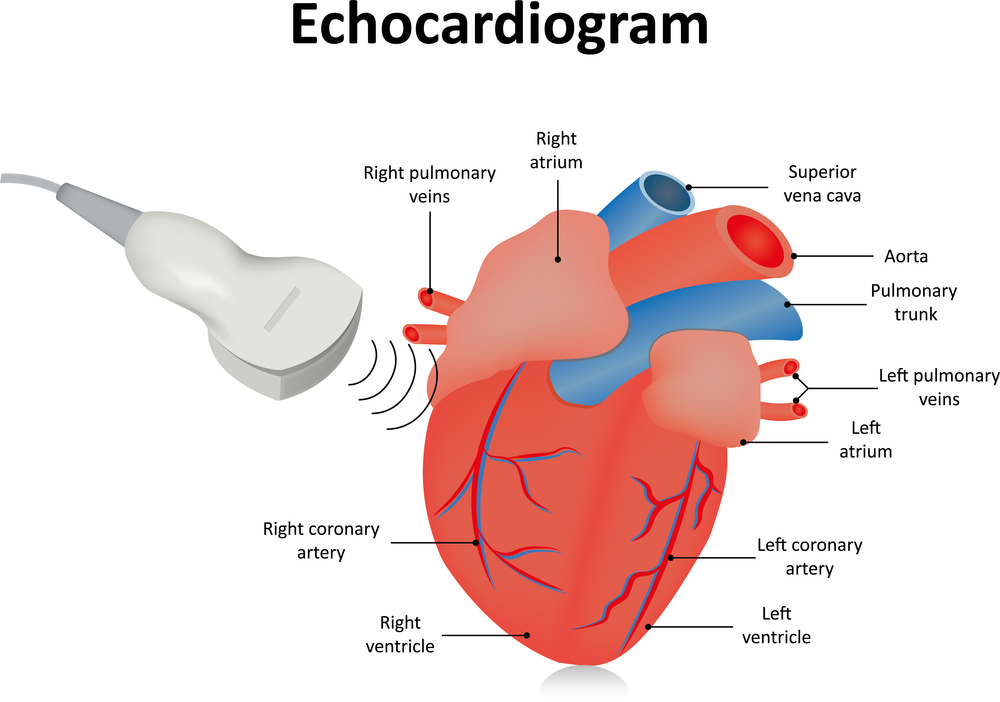
An Echocardiogram (ECHO) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart. It helps doctors evaluate the heart’s structure, function, and blood flow in real time. ECHO is one of the most commonly used cardiac tests because it is safe, painless, and highly informative. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing heart diseases early and guiding proper treatment.
What is an Echocardiogram (ECHO)?
An echocardiogram uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to produce moving images of the heart. These images allow doctors to see how the heart chambers, valves, and muscles are working. It also helps measure the heart’s pumping strength and detect abnormal blood flow.
There are different types of echocardiograms, including:
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) – the most common type
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) – provides more detailed images
Stress Echocardiogram – done before and after exercise
Doppler Echocardiogram – evaluates blood flow through the heart
Doctors recommend an echocardiogram to investigate or monitor various heart-related conditions. Common causes for advising an ECHO include:
1. Chest Pain or Shortness of Breath
These symptoms may indicate heart disease, valve problems, or reduced heart function.
2. High Blood Pressure
Long-standing hypertension can cause heart muscle thickening and reduced efficiency.
3. Heart Murmurs
Abnormal heart sounds may suggest valve disorders that can be confirmed through ECHO.
4. Suspected Heart Failure
ECHO helps assess how well the heart pumps blood (ejection fraction).
5. Valve Disorders
Conditions such as mitral valve prolapse, aortic stenosis, or regurgitation.
6. Congenital Heart Defects
Structural heart problems present since birth can be clearly visualized.
7. Previous Heart Attack
ECHO evaluates heart muscle damage and recovery after a myocardial infarction.
8. Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia)
Helps identify structural causes contributing to rhythm problems.
Symptoms That May Require an ECHO
An echocardiogram itself does not cause symptoms, but it is performed when a person experiences warning signs of heart disease. Common symptoms include:
Chest pain or discomfort
Shortness of breath during activity or rest
Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
Fatigue and weakness
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Dizziness or fainting
Persistent cough or wheezing
Bluish lips or fingertips (in severe cases)
Early evaluation using ECHO can prevent serious complications by detecting heart problems before they worsen.
Prevention: How Can Heart Problems Be Prevented?
While an echocardiogram is a diagnostic tool and not a preventive measure itself, heart diseases that lead to the need for ECHO can often be prevented through healthy lifestyle choices.
1. Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
Limit salt, sugar, and saturated fats
2. Exercise Regularly
At least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week improves heart health.
3. Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Regular monitoring and timely treatment reduce heart strain.
4. Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol
Smoking damages blood vessels and weakens heart muscles.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress contributes to hypertension and heart disease.
6. Regular Health Checkups
Early screening helps detect problems before symptoms appear.
7. Manage Diabetes
Proper blood sugar control protects blood vessels and heart tissue.
By following these preventive steps, the risk of developing serious heart conditions can be significantly reduced.
Treatment: How ECHO Helps in Treatment Planning
An echocardiogram does not directly treat heart disease, but it plays a vital role in guiding treatment decisions.
1. Medication Management
Based on ECHO findings, doctors may prescribe:
Blood pressure medications
Diuretics for fluid retention
Blood thinners
Medications to strengthen heart function
2. Monitoring Disease Progression
ECHO is used regularly to track conditions like heart failure or valve disease.
3. Surgical Planning
Severe valve disorders or congenital defects may require surgery. ECHO helps determine the right time and type of procedure.
4. Lifestyle Modification Guidance
Doctors can recommend activity levels and dietary changes based on heart function.
5. Post-Treatment Evaluation
After surgery or treatment, ECHO assesses recovery and effectiveness.
6. Emergency Diagnosis
In critical cases, ECHO quickly identifies life-threatening conditions like cardiac tamponade or severe heart failure.
Is Echocardiogram Safe?
Yes, echocardiography is extremely safe. It does not use radiation and has no known harmful effects. Most people can return to normal activities immediately after the test.
Conclusion
An Echocardiogram (ECHO) is a powerful and essential tool in modern cardiology. It helps diagnose heart diseases early, evaluate symptoms accurately, and guide effective treatment plans. Whether it is chest pain, shortness of breath, or routine monitoring, ECHO provides valuable insights into heart health without any risk or discomfort.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and undergoing timely cardiac evaluations can significantly reduce the burden of heart disease. If advised by a doctor, an echocardiogram should never be delayed, as early detection can save lives and improve long-term outcomes.